Parallels stellte heute Parallels Mac Management 6 für Microsoft SCCM vor, das den Funktionsumfang von Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) für eine leichtere, effizientere und kostengünstige Verwaltung und Kontrolle von PC- und Mac-Computern über eine zentrale Oberfläche erweitert.
„Das höchste Niveau der Datensicherheit ist heutzutage entscheidend für Unternehmen“, sagte Jack Zubarev, Präsident von Parallels. „Für die zunehmende Verbreitung des Mac in Unternehmen benötigen IT-Admins eine schnelle und effektive Methode, um sowohl Macs als auch PCs über Microsoft SCCM sicher zu verwalten. Parallels Mac Management 6 bietet IT-Abteilungen eine Vielzahl von Tools, mit deren Hilfe es einfach ist, Mac-Berichte anzupassen, die Nutzung zu verfolgen, Arbeitslasten festzulegen und vieles mehr.“
„Als langjähriger Microsoft Partner kennen wir Microsoft SCCM sehr gut und empfehlen Parallels Mac Management für Microsoft SCCM. Durch Parallels Mac Management können Unternehmen ihre vorhandene Hardware mit SCCM nutzen und vermeiden hohe Kosten für eine zusätzliche Infrastruktur. Das Plug-In wird einfach in Microsoft SCCM installiert und die IT-Abteilung kann die Lösung innerhalb von Tagen statt Wochen oder Monaten implementieren. Unsere Kunden sind sehr zufrieden mit Parallels Mac Management und wir sind sicher, dass die neuen Funktionen in Version 6, wie Software-Metering und Remote Lock/Wipe, unsere Kunden begeistern werden.“ Martin Mayr, Senior Vice President, CANCOM GmbH.
Parallels Management Suite for Microsoft SCCM Release Notes Parallels Mac Management v7.1 Update 2 for Microsoft SCCM build PMA2012-7.2.0.18 (October 26, 2018) Parallels Mac Management v7.2 Update 2 for Microsoft SCCM (build PMA2012-7.2.0.18) includes the following new features: Added the ability to register Mac computers in SCCM from the Internet. Ansible is ranked 3rd in Configuration Management with 24 reviews vs Parallels Mac Management for Microsoft SCCM which is ranked 18th in Configuration Management. The top reviewer of Ansible writes 'Check mode enables us to verify that the config we have pushed is what we intended'.
Das Feedback von unseren Version 6 Beta-Testern war sehr gut und wir freuen uns schon, dass alle anderen Kunden ab heute auch die neuen Parallels Mac Management 6 Features testen können. Die komplette Liste von den neuen Parallels Mac Management 6 Funktionen gibt es hier.
„Remote sperren und löschen“ (Remote Lock/Wipe)
Mit der Funktion „Remote sperren und löschen“ (Remote Lock/Wipe) können IT-Manager in Unternehmen einen Mac blockieren oder sämtliche Daten löschen, falls dieser verloren gegangen ist oder gestohlen wurde. Es handelt sich um eine neue Funktion von Parallels Mac Management 6 für Microsoft SCCM zur Erfüllung von Sicherheitsanforderungen, die jetzt auch die Verwaltung der gesamten Nutzungsdauer umfasst.
Software-Metering
Parallels Mac Management 6 unterstützt die Erfassung der Softwarenutzung (Software-Metering) von Microsoft SCCM. So können IT-Manager die Nutzungsdaten von Mac-Clients überwachen und auf Grundlage dieser Daten kostenreduzierende Geschäftsentscheidungen fällen. IT-Admins können jetzt beispielsweise bestimmen, wie häufig Mac-Benutzer jede einzelne Softwareanwendung nutzen können und feststellen, welche Anwendungen am häufigsten verwendet werden. Auch kann festgestellt werden, welche Lizenzen beendet bzw. verlängert werden sollten.
Vom Effizienzstandpunkt aus gesehen, vereinfacht es Parallels Mac Management IT-Managern, Softwarebereitstellungen und -wartungen so einzuplanen, dass die Auswirkungen auf die Benutzerproduktivität und die Netzwerkbandbreite in der Organisation minimiert wird. IT-Manager können außerdem Anwendungsinstallationen und Softwarepaket-Bereitstellung für einen Zeitraum einplanen, wenn ein Mac nicht verwendet wird.
Die Rückmeldungen von Kunden waren der Grund für viele Verbesserungen der Effizienz im Zusammenhang mit den neuen Tasksequenzschritten, die die Funktionen des On-Screen-Displays (OSD) aufwerten, darunter fallen:
- SCCM-Anwendung installieren – Fähigkeit, SCCM-Anwendungen für die macOS-Image-Bereitstellung wiederzuverwenden
- Festplatten formatieren und partitionieren – zum Formatieren und Partitionieren einer spezifischen Festplatte auf einem Ziel-Mac
- Einer Domäne anfügen – verbesserter Support mit einer zusätzlichen Einstellung, die eine mobile Bestätigung erfordert
- Tasksequenzschritt kopieren und einfügen – ermöglicht es IT-Admins, einen Tasksequenzschritt zu kopieren und einzufügen
- Fenster für amodale Tasksequenzeigenschaften – mehrere Tasksequenzen gleichzeitig bearbeiten
- Arbeitslast durch benutzerdefinierte Einstellungen – eine Arbeitslast durch benutzerdefinierte Einstellungen mithilfe des integrierten Editors einem Konfigurationsprofil hinzufügen
- Vorbeugung von doppelten Profilen – prüft, ob ein Konfigurationsprofil bereits als Teil einer Baseline angewendet wurde und ob alle Einstellungen korrekt durchgesetzt wurden
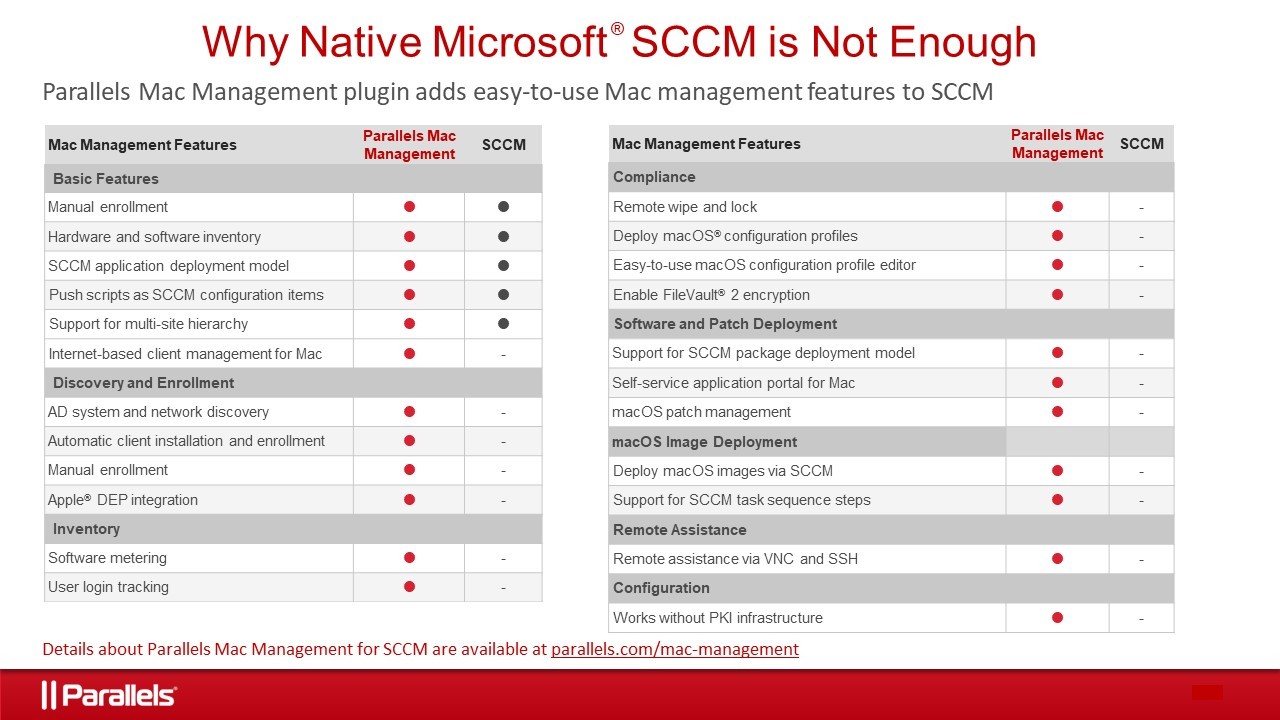
Mit Parallels Mac Management 6 für Microsoft SCCM können IT-Admins, Systemarchitekten oder CIOs schnell und kostengünstig die vorhandene Microsoft SCCM-Infrastruktur erweitern, um Macs und PCs über eine Oberfläche zu kontrollieren. IT-Abteilungen stehen jetzt mehr Tools zur Verfügung, um die Sicherheit und Effizienz zu erhöhen und sogar Unternehmensentscheidungen zu erleichtern, ohne dass dabei Kosten für zusätzliche Infrastruktur entstehen.
Unser Vertriebsteam stellt gerne weitere Informationen zu Parallels Mac Management bereit.
In Part 1 of the Parallels Mac Management for SCCM series I installed the Parallels Configuration Manager Console Extension. I installed this on my site server ‘ConfigMgr’.
Part 2 focused on the installation of the Parallels Proxy which I installed on a remote server called ‘Parallels’ which I intend to use to install the Parallels roles.
Part 3 of the series concluded the ‘role’ installation, namely the NetBoot Server and OS X Software Update Service.
Part 4 of the Parallels series focused on getting the Parallels Mac client onto a Mac OS X device.
In Part 5 of the series I will show you how to deploy an application down to a Mac OS X device, install it via the app portal and remove the application.
Set up the CMAppUtil tool
Before we can configure the application in ConfigMgr we need to convert the deployment onto a format that ConfigMgr can consume. To achieve this we need the CMAppUtil tool provided by Microsoft as part of the ConfigmgrMacClient.msi. This can be downloaded from here. Click the Download button.
Select the ConfigmgrMacClient.msi and click Next.
Once downloaded run the MSI on a Windows device to extract the contents of the file into a dmg file that can be used on a Mac device. Click Next.
Agree to the licence agreement and click Next.
Make a note of the location the files will extract to and click Next.
Continue through the wizard to completion. Browse to the location C:Program Files (x86)MicrosoftSystem Center Configuration Manager for Mac client if you have installed into the default location. Copy the macclient.dmg over to a Max OS X machine.
Once the dmg file is on the Mac, double-click the file to see its contents. Extract the Tools folder from the file by dragging and dropping it to a folder on your Mac.
The CMAppUtil is the utility we will use to convert a Mac package into a .cmmac file that ConfigMgr can use. CMAppUtil supports the .dmg, .pkg, .mpkg, .app file formats.
In this example, I have downloaded the WinZip 5 for Mac application and placed the .dmg file for the WinZip install into the same folder as the CMAppUtil file.
Converting to .cmmac
Load up Terminal on the Mac by launching Finder and navigating to Applications>Utilities.
To convert a dmg to the .cmmac format use the following command:
The -c option specifies the source file being converted. The -o option specifies the output path. The -s is not required but I used it to fix some issues extracting out the content of the .dmg and is worth including.
After the process has completed you will have a .cmmac file that can be consumed by ConfigMgr. Copy the .cmmac over your ConfigMgr source content share.
Creating the application
In the ConfigMgr console, go to the usual location where you would create an application, in the Software Library>Overview>Application Management>Applications node. Right click and choose Create Application.
In the Create Application Wizard choose the Automatically detect information about this application from installation files checkbox. From the Type drop down choose Mac OS X and then enter the network location for the .cmmac file. Click Next.
Click Next.
Enter the relevant information about the application and click Next.
Click Close to complete the wizard.
To specify the command that you want to use to install, and optionally uninstall, the application on a Mac, right click the Deployment Type and select Properties.
On the Programs tab enter a command to install and remove the application.
Use the following syntax:
As an example, the following command line contains the installation and uninstallation commands for Firefox (note the colon characters, which are required):
:/usr/bin/ditto “Firefox.app” “/Applications/Firefox.app”:rm -rf “/Applications/Firefox.app”:
The first section :/usr/bin/ditto “Firefox.app” “/Applications/Firefox.app”: installs the Firefox.app into the Applications/ folder.
Mac Management Ventura
The second section rm -rf “/Applications/Firefox.app”: removes Firefox from the Mac device.
Therefore, for my installation of WinZip, I have used the command
Distribute the content to a Distribution Point and then right click the newly created application and choose Deploy. Target the deployment at a Mac based collection, here I have chose the All Mac OS X Systems collection.
Since I am going to use the Parallels Application Portal, I will make the application available.
Installing and Removing via the Parallels Application Portal
Once policy has applied to the Mac OS X device, remember this can be forced by clicking Connect in the Parallels Mac client or you can wait the default of 60 minutes for updates to be checked automatically, then head over to the Parallels Application Portal.
The portal is located in the Applications folder in Finder.
The application will be available to you. Click Install.
Once installed, the application will be available to you in the location you installed it to.
Sccm Mac Client
To uninstall the application, click the Remove button in the portal.
If you receive any failures, or just want to have a nosy in the log files then the pma_agent.log file located in /Library/Logs is the one to check. The log snippet below, for example, showed a problem locating the content on the DP. A quick redistribution of the content to the DP fixed the problem.
In Part 6 of the series, I take a look at deploying packages via Parallels. Packages can be used in Task Sequence deployment in the Parallels Mac Management product, whereas applications cannot, so it is worth looking both application models.